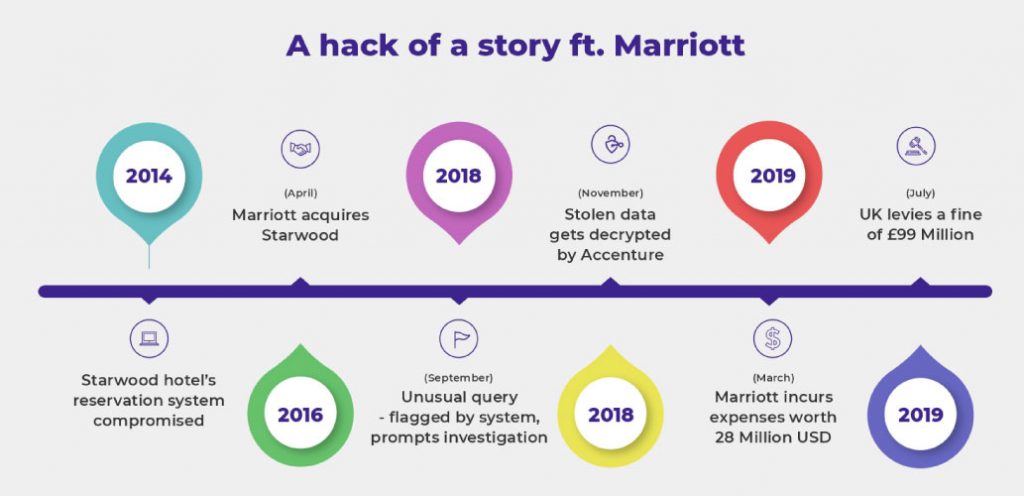
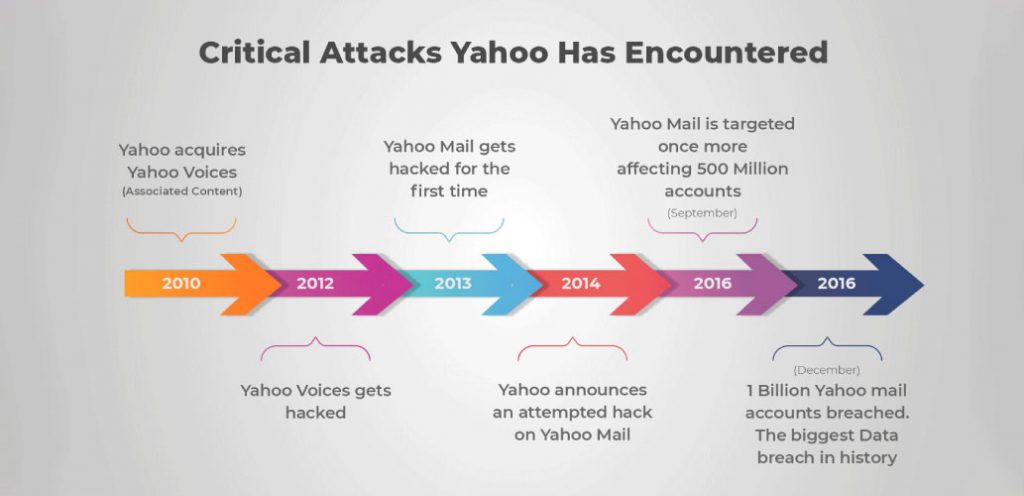
If you’ve started or are planning to start a career in Business Analytics, let us give you a fair warning. It can get pretty overwhelming quickly. There are large chunks of data to go through in very little time, and watching your peers accomplish it in seconds can lead to a whole new level of FOMO.
So here’s our suggestion.
Why not pick up these top 3 Business Analytics tools for freshers? They’re easy to learn, used in practically every organisation and are sure to give you an edge over others.

Microsoft Excel for data anaysis
Ouch! We apologise for the oldest Excel joke in the book. And we’re sure you must also be laughing at the suggestion of learning Excel because it can look and feel very basic.
But don’t get fooled by its easy interface. Excel is a powerhouse of features that allows you to:
- Collect data
- Perform statistical analysis
- Make complex reports
- Integrate with other Business Intelligence tools like Power BI
In fact, its user-friendly interface is what has made Excel the most preferred Business Analytics tool in all organisations. If you’re not familiar with some of the more analytical features of Excel, we recommend you start exploring these functionalities as a starting point:
Text to Column
As a future Business Analyst, you should know that you will not always have the luxury of getting your data in nice little columns as you’d like. More often than not, the data will be mixed up and you may have to separate them. For example, you may need to split customers’ full names into their first names and last names or separate out the year from the date of birth. In such cases, you can simply select the column, select Data >> Text to Column and specify the delimiter. (In names, first name and last name are separated by space, so the delimiter is space. The different parts of the date, like 27/07/2015, are separated by /. So the delimiter, in this case, is ‘/’)Concatenate
A near opposite to the Text to Column, the concatenate feature of Excel allows you to combine two columns into one – for example, a column containing the first name and another column containing the last name can be concatenated automatically into a new column with the full name.Sorting & Filtering
The sort and filter functions are going to be your handy assistants in the years to come. As a Business Analytics professional, you will constantly have to sort data in a particular order or filter out certain conditions, like regions, age groups, etc. and Excel allows you to perform these functions with ease.VLookup
Vertical Lookup, more commonly known as VLookup, is another useful feature in Excel that enables users to find specific values in columns. Vlookup is beneficial in creating reports as it helps with combining data from two different spreadsheets into one.Pivot Tables
Pivot tables allow you to create specific, condition-based summaries easily. For example, from your inventory records, if you want to analyse your consumer’s top 3 product buys in metro cities, you don’t have to manually segregate the data. You can simply apply a pivot table to the range of the data and you’ll get the results. What’s more, you can also convert it into a Pivot Chart to get a visual representation of the data for the purpose of presenting.
These are just some of the everyday yet powerful features of Excel. As you get deeper into it, you will find more functionalities that will help you in your day-to-day job. Excel, by itself, is great. But when Excel is combined with other tools, the world is your oyster!

Visualise with Tableau
The axiom “a picture is worth a thousand words” will soon become your favourite as you’ll start working on large volumes of data. Luckily, Tableau should help you out in the endeavour. Where Excel is essentially a spreadsheet tool that allows you to analyse data and perform calculations, Tableau is famous for its data visualisation abilities.
Founded in 2003, Tableau is one of the most popular and fast-growing tools used in Business Analytics and Business Intelligence today. It manages vast volumes of data and its flow and turns data into actionable information. It allows you to analyse and visualise data faster and more efficiently. Tableau accomplishes this with the Tableau Product Suite which consists of:
- Tableau Desktop
- Tableau Public
- Tableau Online
- Tableau Reader
There are many reasons why Tableau is the preferred choice for Business Analysts:
✔ For one, Tableau is really easy to understand. It has a very simple interface and its learning curve is generally regarded to be short. Hence, even as a beginner, you can pick up on the skills and stand out from your peers.
✔ Tableau can handle large volumes of data and can connect to 40 different data sources including local text files, Microsoft Excel, PDFs, JSON or databases and servers like MySQL Server, Microsoft SQL Server, among others.
✔ Tableau has an easy-to-use drag-n-drop feature which allows users to create interactive dashboards with just a few clicks.
✔ Tableau provides convenient options to collaborate with other users and instantly share data in the form of visualisations, sheets, dashboards, etc. in real-time
✔ The Ask data feature of Tableau makes it even more favoured by users globally. It’s the Google search version on our reports. All you need to do is to type your query about the data in natural language and you’ll get the most relevant answers from Tableau.
So, in a nutshell, Tableau is great. But Tableau is not the only Business Analytics tool in the market there. In fact, if you’re comfortable with the Microsoft interface, there is another platform, you must check out – Power BI.

Power up with Power BI
Tableau has a great range of products and is considered to be a very powerful tool, but it is also equally expensive. For beginners, whose access to data and need for analysis is reasonably limited, Power BI is a viable alternative. That, combined with its price which is almost 1/7th of Tableau, makes Power BI the go-to platform for Business Analytics.
Like Tableau, Power BI is also used for data visualisation. It comes with standard data visuals that you can make use of to build interactive reports, such as bar, column, line, map, matrix, pie charts, scatter, table and waterfall. Each of these visuals has its options for customisation to enhance presentation and functionality.
While it doesn’t support as many data sources as Tableau, Power BI allows you to connect to:
- Cloud-based sources such as DropBox, Azure (Azure Data Warehouse), OneDrive, Google Analytics, and SalesForce,
- Excel spreadsheets and CSV files
- Data located on-premises, such as SQL Database
Further, Power BI is very famous for its natural language querying capabilities, where you can ask specific queries like “How did the sales team perform last quarter?”. All you have to do is double-click an empty part of your report canvas and use the ‘Ask a Question box’.
The best part about Power BI is that it has been created by Microsoft, which allows for easier integration with Microsoft applications, especially Excel.
Although Power BI is about 10 years younger than Tableau and has lots to grow for seasoned Business Analysts to work comfortably with, it’s an extremely comfortable, affordable platform for beginners and is sure to become powerful in the coming years.
Well, these are the top 3 platforms for beginner Business Analysts. You can learn more about them in depth and understand their real-world applications in our Business Analytics Certification program designed for college students.
Is there any platform you’d like to know more about in detail? Let us know in your comments below.