In the digital climate we live in today, blockchain technology has become a transformative tool with the ability to influence various industries! Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a blockchain developer, or curious about the technology that underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin; understanding the building blocks of blockchain is a fundamental step.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the core components that make up this innovative technology. We’ll break down the complexities, demystify its different aspects, and provide you with a clear understanding of how blockchain works. So, let’s unravel the building blocks of blockchain together!
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
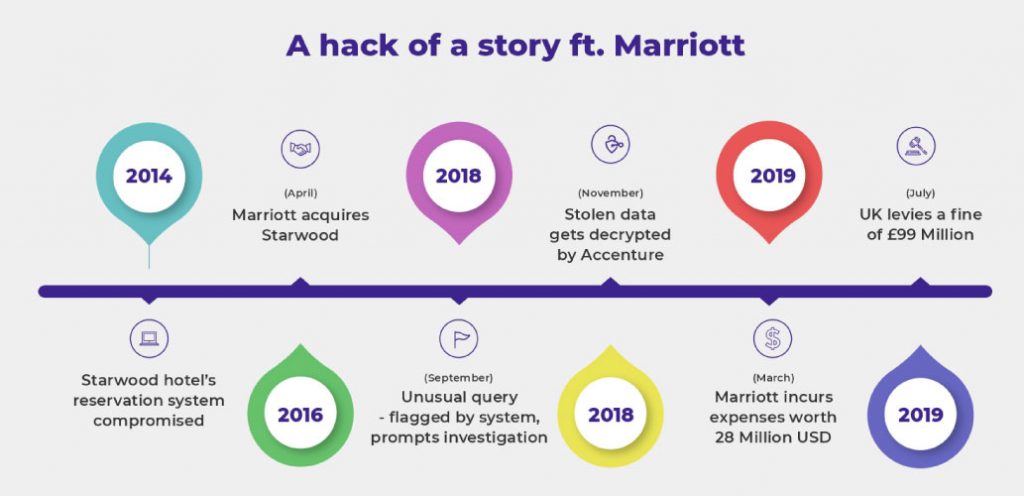
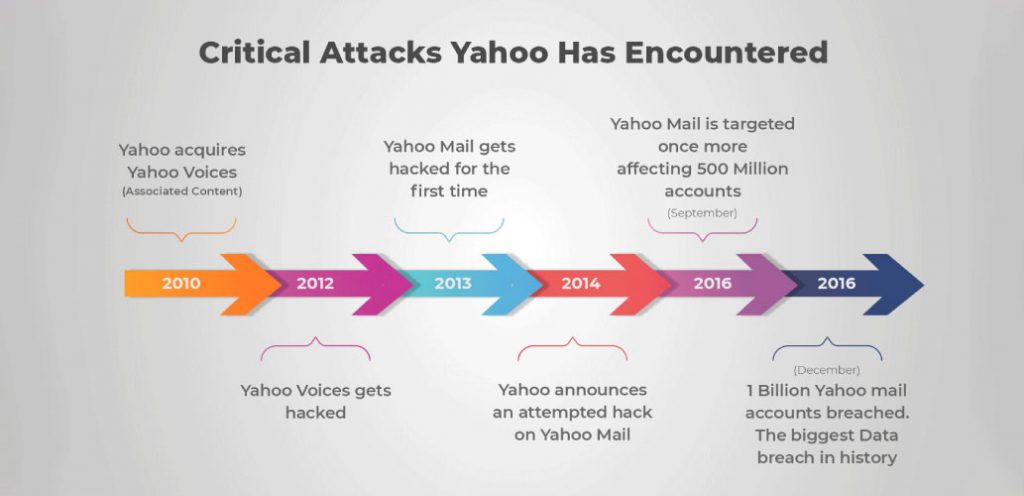
Blockchain technology might have become mainstream recently, but its research had actually begun in the 1990’s. However, it wasn’t until 2009 – when Bitcoin was created – that the technology was actually implemented.
Bitcoin, as we all know, is the world’s first cryptocurrency. And initially, blockchain only served as the backbone of cryptocurrency. Eventually, it was discovered that blockchain technology can actually be separated from Bitcoin and be used in other ways as well.
Blockchain Made Simple
In the simplest terms, blockchain is made of multiple small blocks of information that are linked together. These blocks of information are called ledgers. Visualize a storekeeper making an inventory, recording all goods coming in and going out of the store. Each unit sold is noted, including details like the date of purchase, expiry date, and supplier’s name.
Blockchain stores relevant information that is transparent and visible to everyone in that network. Each page in the inventory book is equivalent to one block. In the case of Bitcoin, transaction details are stored in each block.
Understanding Bitcoin
Let’s understand this with a group scenario – Tom, Jerry, Mike, and Bruno. They decide to use cryptocurrency for transactions. Jerry, the first to pay, creates a block with the transaction permanently inscribed, including the number of Bitcoins sent and the group’s individual balances.
Each block contains a unique hash number, like a unique fingerprint generated based on the information stored. This hash number helps track the history of the entire chain.
How does this Block form a chain
Blocks form a chain because, along with the hash of the current block, the hash of the previous block is also displayed. As a new block is created, it contains a new hash and the hash of the previous block. This creates a chain where each block references the one before it.
Using hash numbers, you can track the history of the entire chain. The blockchain or ledger is public, allowing anyone in the chain to view the complete transaction history.
Security Measures
Now you might be wondering what makes Blockchain so secure? One can’t simply change transaction details. The hash is unique to the data inscribed in a block, not the block itself. If you change data in a block, the hash changes, making the whole chain invalid because the data does not match.
One could argue that changing the hash in all blocks isn’t viable due to the time it takes to change data in a block. Additionally, the blockchain or ledger is publicly distributed, and changes require consensus from the group.
The Bottom Line
Blockchain technology has been around for a while now, and this is just the beginning, with such a boost in interest from blockchain developers around the world! Industries have adopted this technology to better facilitate their businesses, and it’s fascinating to see how blockchain will be used globally in the coming decades.
What are your thoughts on blockchain? Let us know in the comments below.
Exploring Blockchain Further
Blockchain technology has recently seen a boom in popularity, and this is just the beginning. With a surge in interest from blockchain developers worldwide, it’s clear that the power of this transformative technology is only going to increase going forward. It’s a good idea to invest your time in learning blockchain and understanding the different types of blockchain, as well as their applications.
If you aspire to become a blockchain developer, consider exploring blockchain certificate courses. These courses take you through the building blocks of blockchain technology and help you understand how to harness the potential of this powerful technology.
Also Read: What’s up with Web 3.0?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How Many Blocks are in Blockchain?
A: There can never be a fixed number of blocks in a blockchain. The number of blocks is continually increasing as new transactions are added to the network, forming a chain.
2. Who Creates Blocks in Blockchain?
A: Blocks are created by individuals known as “miners” who use computational power to solve intricate mathematical challenges in a process known as proof-of-work (PoW).
3. What is the Name of the Block in the Blockchain?
A: Blocks are identified by their position in the chain, usually with a unique block number or block height. The first block is called the Genesis block or Block 0.
4. What are the Three Parts of a Block in a Blockchain?
A: The three parts of a block in a blockchain are Block Header, Transaction Data, and Block Hash.
5. What are the Four Features of a Blockchain?
A: The four features of blockchain technology are Decentralization, Transparency, Security or Encryption, and Integrity of Ledger.